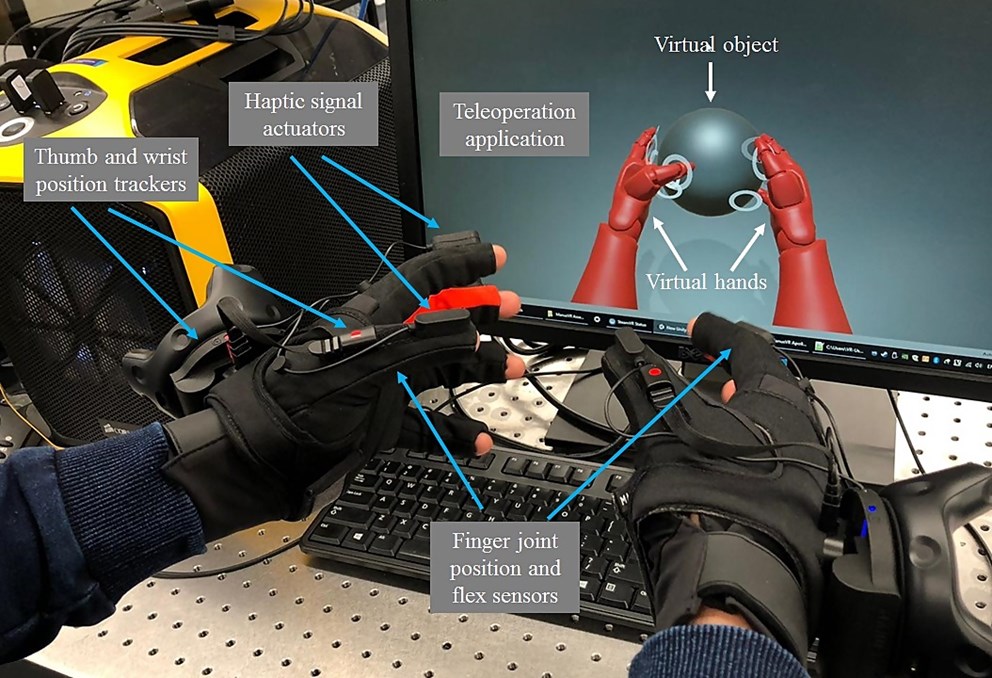
Haptic technology
Haptic is the science that is responsible for the study of the sense of touch, so the haptic devices are responsible for simulating tactile responses, that is, by using these devices, the presence of three-dimensional objects can be perceived in a virtual environment.
It is also known as 3D touch or kinesthetic communication, and seeks to
create experiences using vibrations, movements and other forces. Since touch is
the most fundamental method of interaction, harnessing the sensations in your
products is quickly becoming the newest approach to creating memorable brand
experiences.
The main purpose of the haptic is to act as a form of tactile
communication between an inanimate object and a human being, allowing inanimate
objects to recreate the sensation of using real objects and, in turn, these
inanimate objects to restore touch.
What are its main uses?
The haptic has gradually expanded, reaching new uses. Currently we can
find four: vibration, button stimulation, thermal and kinesthetic.
On the one hand, we have vibration, which is what most haptic devices
are focused on. Technologies such as resonant linear actuators (LRA) and
eccentric rotating mass (ERM) create much of the haptic experiences found on
mobile and portable devices.
These are based on an internal component responsible for producing the
movements, although the LRA have gained more fame since the sound they generate
is almost greater than the sensation of vibration.
Smart displays do not naturally offer a tactical response as simple as a
mechanical button. And is that, these can get to use haptic and sound feedback
to mimic the feeling of a mechanical pressure pad under the finger.
On the other hand, we have thermoelectric effects, which can create
haptic experiences based on temperature. By manipulating the flow of electrical
current between the alternating conductors of a device (one hot and one cold),
users can experience different temperatures.

Comments
Post a Comment